The AMD Ryzen 5 8600G is an affordable APU that will offer you gaming capabilities, without the need of a dedicated GPU, given that your demands are not high. It has six cores and 12 threads, so it won’t have a problem handling everyday tasks, and it also comes with an unlocked multiplier, which offers some interesting results.
You will find all Zen 4 CPU and APU reviews I have done so far below:
- AMD Ryzen 9 7950X3D
- AMD Ryzen 9 7900X
- AMD Ryzen 9 7900
- AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D
- AMD Ryzen 5 7600X
- AMD Ryzen 5 7600X (on MSI MAG B650M Mortar)
- AMD Ryzen 7 8700G
The fresh Ryzen 7/5 APUs, the 8700G, and 8600G, respectively, use the monolithic “Hawk Point” silicon, and today, January 31st, is their launch date. Both have embedded Radeon graphics, 780M and 760M respectively. They only have PCIe 4.0 support, which might be a letdown for some users. These new CPUs will be supported by all mainboards based on the AMD X670/E, B650/E, and A620 chipsets, with the required firmware updates. Once I got my samples, I first tried an ASUS TUF GAMING X670E-PLUS. The system didn’t boot with the current BIOS, so I used the mainboard that AMD sent me along with the CPUs, a Gigabyte B650 AORUS Elite AX, which had a special BIOS installed to be able to boot with the new CPUs.
The Ryzen 7000 chips have integrated graphics but with low-performance iGPUs, and this is why AMD doesn’t call them APUs* but CPUs. On the other hand, the 8700G has a strong iGPU, so it deserves to be named APU.
*An APU (Accelerated Processing Unit) is a type of processor that combines both a CPU (Central Processing Unit) and a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) onto a single chip.
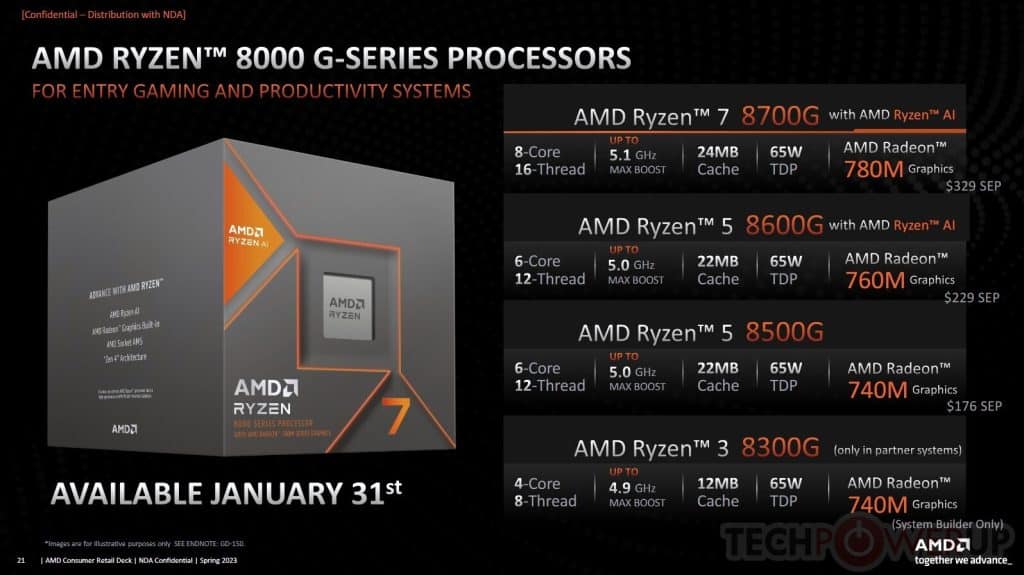
AMD’s Ryzen 8000G series debuted with four models, which are listed below:
| Model | Cores/Threads | Boost6 / Base Frequency | Total Cache | TDP | NPU | SEP | |
| AMD Ryzen™ 7 8700G | 8C/16T | Up to 5.1GHz / 4.2GHz | 24MB | 65W | Yes | $329 | |
| AMD Ryzen™ 5 8600G | 6C/12T | Up to 5.0GHz / 4.3GHz | 22MB | 65W | Yes | $229 | |
| AMD Ryzen™ 5 8500G | 6C/12T | Up to 5.0GHz / 3.5GHz | 22MB | 65W | N/A | $179 | |
| AMD Ryzen™ 3 8300G | 4C/8T | Up to 4.9GHz / 3.4GHz | 12MB | 65W | N/A | N/A | |
AMD sent me the CPUs without any material or information for unknown reasons, so I was forced to dig most of the info from what my friends at TechPowerUp mentioned in their detailed news post here.
The 8700G and 8600G are based on the 4 nm “Hawk Point” silicon, featuring Ryzen AI, and are the first desktop processors to feature an NPU (neural processing unit). The 8500G and 8300G are based on the 4 nm “Phoenix 2” silicon. The Ryzen 7 8700G leads the pack and is the flagship implementation of “Hawk Point,” featuring an 8-core/16-thread CPU based on the “Zen 4” microarchitecture, the full Radeon 780M integrated graphics implementation with 12 RDNA3 compute units, and the Ryzen AI XDNA NPU. The processor has a combined AI throughput of 39 TOPS, with 16 TOPS from the NPU.
The 8-core/16-thread CPU of the 8700G is clocked at 4.2 GHz base and 5.1 GHz maximum boost frequency. Each of its eight cores has 1 MB of L2 cache, and the eight share a 16 MB L3 cache. The Radeon 780M iGPU has an engine boost frequency of 2.9 GHz. This GPU has twelve compute units, 768 stream processors, 24 AI accelerators, 12 Ray accelerators, 48 TMUs, and 32 ROPs. The TDP is kept relatively low, given the strong iGPU, at 65W. AMD sells it in a package with a Wraith Spire cooler, which can handle up to 95W TDP processors.
The Ryzen 5 8600G is based on the same “Hawk Point” silicon as the 8700G but has fewer cores and threads (6-core/12-thread). Its “Zen 4” CPU is clocked at 4.35 GHz base with an up to 5 GHz boost clock. Each of the six cores has 1 MB of L2 cache and shares the 16 MB L3 cache. In this APU, we find the Radeon 760M integrated graphics. The 760M has 8 compute units, 512 stream processors, 16 AI accelerators, 8 Ray accelerators, 32 TMUs, and 16 ROPs. AMD has given it a maximum engine boost frequency of 2.8 GHz. The 8600G uses the same NPU as the 8700G, with an identical 16 TOPS throughput. The TDP rating is the same at 65W, and AMD also includes a Wraith Spire cooler in the PIB retail package.
Some information on the 8500G and 8300G, which I won’t cover in this review. These are not based on 178 mm² “Hawk Point” silicon but the smaller 137 mm² “Phoenix 2.” This chip physically features a 6-core CPU, but from these, two are “Zen 4” cores, while the other four are “Zen 4c,” making this AMD’s first hybrid processor. The “Zen 4c” core is physically smaller than “Zen 4” and was initially designed for the high-density 128-core EPYC “Bergamo” server processor. Despite being physically smaller, it has identical numbers of core components as “Zen 4” and hence has an identical IPC and instruction set as “Zen 4,” as well as SMT. However, it has much tighter vCore limits, meaning these cores have a lower boost frequency than the “Zen 4” cores. AMD marks the “Zen 4” cores as UEFI CPPC “preferred cores,” which tells the OS to prioritize workloads to them, as they can hold on to the highest boost frequencies.
Besides the fewer cores, the “Phoenix 2” silicon also lacks an NPU, meaning the 8500G and 8300G won’t have Ryzen AI. Moreover, they have the less capable 740M iGPU, which physically only has 4 compute units, 256 stream processors, 8 AI accelerators, 4 Ray accelerators, 16 TMUs, and 8 ROPs—the iGPU’s boost frequency is set at 2.8 GHz on the 8500G and 8300G.
The Ryzen 5 8500G is a 6-core CPU with 12 threads. As mentioned above, two of these cores are “Zen 4,” and the other four are “Zen 4c.” Each core has a 1 MB L2 cache, with all six sharing the 16 MB L3 cache. The Ryzen 5 8500G CPU has a base frequency of 3.5 GHz, with a maximum boost frequency of 5 GHz, which can be achieved only by the “Zen 4” cores. There is no information yet on the maximum boost frequency of the “Zen 4c” cores. The retail PIB package of the 8500G will include a Wraith Stealth cooler, a compacted version of the Wraith Spire designed for 65 W processors.
The Ryzen 3 8300G is an entry-level chip that AMD isn’t releasing in the retail channel but only through its prebuilt desktop OEM partners. It includes a 4-core CPU, but only one of the four cores is “Zen 4,” the other three are “Zen 4c.” The CPU base frequency is 3.4 GHz, and the maximum boost frequency is up to 4.9 GHz, which can only be achieved by the single “Zen 4” core. The 8300G gets the same Radeon 740M iGPU as the 8500G, with an identical 2.8 GHz boost clock. TDP remains the same at 65W.
Specifications
- Model Number: AMD Ryzen 5 8600G
- Architecture: Zen 4
- Cores: 6
- Threads: 12
- CPU Compute Die (CCD) Size: 178mm²
-
Package Die Count: 1x
- Base Clock: 4.3GHz
- Boost Clock: Up to 5.0GHz
- Default TDP: 65W
- PCI Express Version PCIe 4.0: 20 / 16
-
Native PCIe® Lanes (Total/Usable)
- Memory Type: DDR5
- ECC Support: Yes
-
Memory Channels: 2
- Unlocked for Overclocking: Yes
- L2 Cache: 8MB
- L3 Cache: 16MB
- Lithography (CPU Cores): TSMC 4nm FinFET
- Max Operating Temperature (Tjmax): 95°C
- Graphics Model: Radeon 760M
- Graphics Core Count: 8
- Graphics Frequency: 2800 MHz
-
DisplayPort/HDMI Version: 2.1
- Bundled Cooler: –
- Socket: AM5



The 8600G does include a cooler, it includes the wraith stealth