Storage was always crucial for the end user. As time passes and apps and games require more space, the more storage options you have, the better. Only Sky and our budget are the limits on internal and external storage options. But sometimes, even the space we have might be inadequate. And then, we need to free up some space. Do you know there are more options than deleting and uninstalling to manage our storage? In this article, I will show you how to manage your Windows 11 space like a pro. More free-space options are always welcome. The most important thing is that you don’t need third-party tools. Microsoft offers us all the tools we need.
Windows Storage Options
The easiest way to check your space is to use the default Windows 11 options. To do so, go to your Windows icon near the search bar, right-click on it, and choose “Settings.”
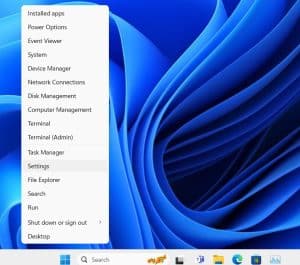
Next, select “Storage” from the “System” menu.
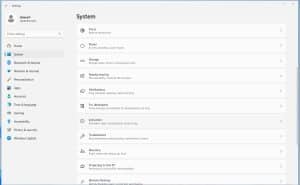
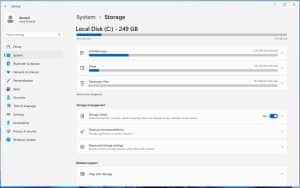
From there, you can see the space used in categories, etc. You can delete what you don’t need, such as temporary files. If you have more than one drive, you can also select the one you want to check. Moreover, you can click on “Advanced storage settings” if you need to. It is a welcome feature for the average user. The best thing is that you don’t need third-party tools. Microsoft has you covered.
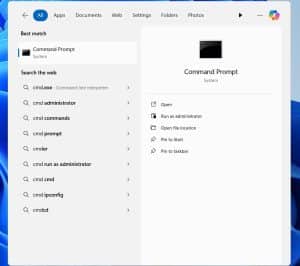
The CMD way
If you are a more advanced user or want to try other methods to check your storage, then the CMD section is for you. It is not math but requires a bit of advanced command skills. Don’t worry; you won’t destroy your computer if you make a mistake. The most likely thing is that the command won’t run in the worst-case scenario. So, feel free to test your skills. You will first need to open Command Prompt and “Run as admin”. The most convenient way is by clicking on the “Search bar”, typing CMD, and selecting “Run as admin”, as shown in the images below.

Diskusage
Now that we have CMD running, the command we shall use is diskusage. Diskusage is a convenient tool for analyzing our storage usage. You can find the file you want and copy it as a path (right-click on it > “copy as path”. Important: Delete all ” when you paste it as a path. E.g. if you copy “C:\ Desktop”, you should paste it as C:\ Desktop without the quotes, or select it and paste it on the CMD). The command type is diskusage Location /h. For example, in the image below, I want to analyze the size of a folder on my Desktop. The final command will be (after System32>): diskusage C:\Users\JimmyV\Desktop\screen /h and then “Enter”. The final result will be shown as in the image below.
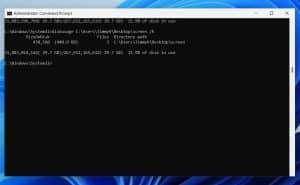
minFileSize Parameter
If you want to add a specific minimum size as a parameter, then the output will be diskusage /minFileSize=file’s size Location /h (where the file’s size will be the size we want to set as a minimum). In the example below, I want to check files larger than 1MB. The final command will be: diskusage /minFileSize=1024 C:\Users\JimmyV\Desktop\screen /h and hit “Enter”.
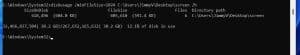
u=Number or t=Number Parameter
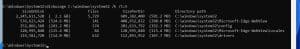
If you want to see the size of the top files in a location, the command type should be diskusage Location /h /u=Number or t=The number you wish to see in descending order. In the example below, I want to see the top 5 files in the System32 location (you can choose u=4, 6, 10, etc., whatever you want to see). The final command will be: diskusage C:\windows\system32 /h /u=5.

Similarly, if I want the folders’ size, the final command will be: diskusage C:\windows\system32 /h /t=5.
From now on, you are ready to master the Windows 11 storage options like a pro or analyze them if necessary. There is no need for third-party tools; it’s just a bit of an extra learning curve. Microsoft has you covered. I hope the same for this article. Better storage management is always welcome.


