Part Analysis
| General Data | |
| Manufacturer (OEM) | CWT |
| Platform | CSA |
| PCB Type | Double-Sided |
| Primary Side | |
| Transient Filter | 4x Y caps, 2x X caps, 2x CM chokes, 1x MOV, 1x Power Integrations CAP200DG (X Capacitor Discharge IC) |
| Inrush Protection | NTC Thermistor SCK-207R0 (7 Ohm @ 25°C) & Relay |
| Bridge Rectifier |
2x Yangzhou GBUU2508 (800V, 25A @ 110°C)
|
| APFC MOSFETs |
3x Way-On WML53N60C4 (600V, 26A @ 100°C, Rds(on): 0.07Ohm)
|
| APFC Boost Diode |
2x CRMicro CRXI06D065G2 (650V, 6A @ 167°C)
|
| Bulk Cap(s) |
2x Nippon Chemi-Con (400V, 470uF each or 940uF combined, 2000h @ 105°C, KMW)
|
| Main Switchers |
4x PingWei PWE120N65SFMF (650V, 20A @ 100°C, Rds(on): 120mOhm)
|
| APFC Controller | Champion CM6500UNX |
| Resonant Controller |
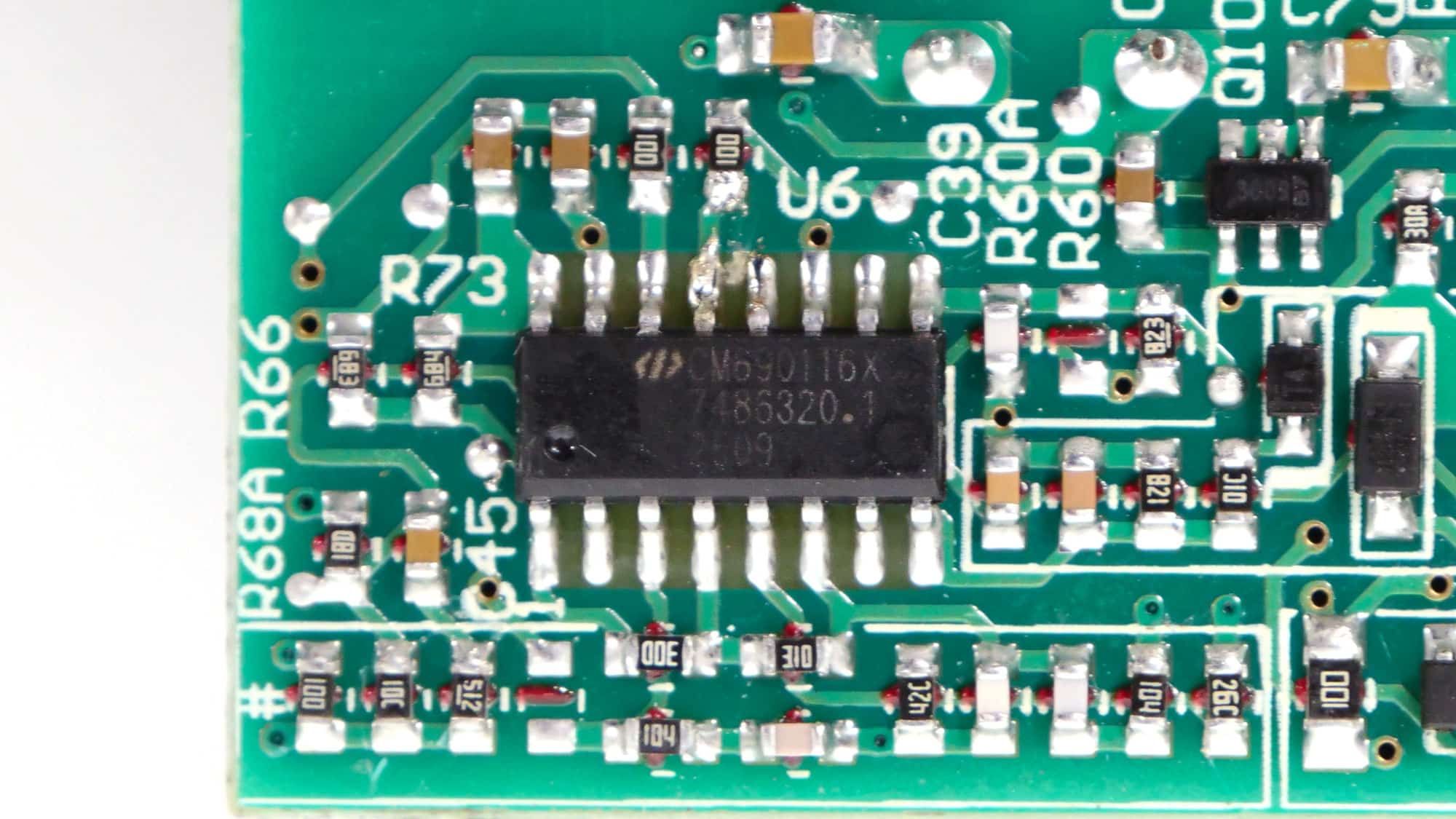
Champion CM6901T6X
|
| Topology | Primary side: APFC, Full-Bridge & LLC Resonant Converter Secondary side: [12V] Synchronous Rectification & [Minor Rails] DC-DC converters |
| Secondary Side | |
| +12V MOSFETs | 8x PingWei PWC013N04ES (40V, 155A @ 100°C, Rds(on): 1.3mOhm) |
| 5V & 3.3V | DC-DC Converters: 4x UBIQ Semi QM3054M6 (30V, 61A @ 100°C, Rds(on): 4.8mOhm) PWM Controller(s): ANPEC APW7159C |
| Filtering Capacitors | Electrolytic: 4x Nippon Chemi-Con (@ 105°C, W) 2x Rubycon (6-10,000 @ 105°C, ZLH) 2x Rubycon (4-10,000 @ 105°C, YXF) Nichicon (4-10,000 @ 105°C, HE(M)) Nichicon (5-6,000 @ 105°C, HV(M)) Polymer: 24x Toshin Kogyo, 1x Nippon Chemi-Con |
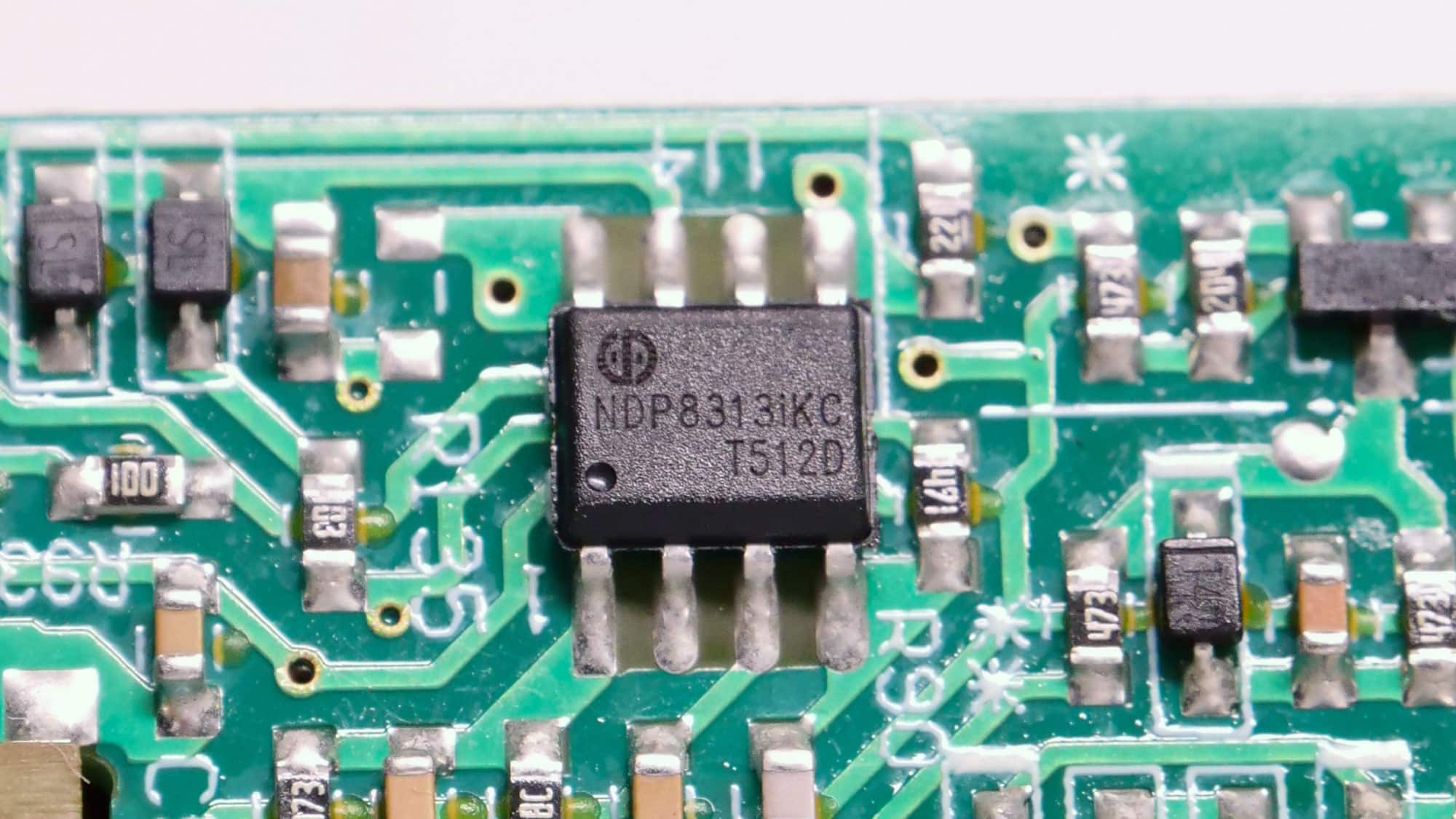
| Supervisor IC | NDP NDP8313iKC |
| Fan Model | TT-13525 / CWT13525H12F-9 (135mm, 12V, 0.4A, Fluid Dynamic Bearing Fan) |
| 5VSB Circuit | |
| Rectifier (Secondary Side) |
Dongke DK5V45R10V (45V, 10mOhm)
|
| Standby PWM Controller |
Biyi Micro KP22306AWG
|
CWT provides the platform, featuring a contemporary design with a full-bridge topology on the primary side and an LLC resonant converter for reduced energy losses. The PCB is tiny for a 1200W unit, and to keep the parts cool without overspinning the fan, CWT used large heatsinks on the primary side. Typically, for a CWT design, the heatsinks on the secondary side are way smaller. Basically, the secondary’s side heatsink is a plate surrounding three sides of the main transformer, providing cooling and acting as a common-mode EMI shield. The same aluminum cover of the main transformer also offers limited high-frequency magnetic shielding.
To keep costs low, CWT didn’t use branded FETs from Infineon or Vishay but went with Chinese brands that will do just fine. On the other hand, for the electrolytic capacitors, it chose well-known and expensive brands. Moreover, the cooling fan is provided by CWT, which decided to make its own rather than rely on other manufacturers. This is a wise move!
The transient filtering stage contains all the necessary components to block both incoming and outgoing EMI emissions. Typically, it starts at the AC receptacle and continues on the main PCB. It also includes a discharge IC for its X caps to provide a slight efficiency boost.
There is an MOV to protect from voltage surges and an NTC thermistor with a resistance of 7 ohms. Moreover, a bypass relay supports the NTC thermistor.
The parallel bridge rectifiers convert the incoming AC signal to a loosely regulated DC voltage. Combined, they can handle up to 50A.
The APFC converter uses three Way-On WML53N60C4 FETs and two CRMicro CRXI06D065G2 boost diodes. Nippon Chemi-Con manufactures the bulk capacitors. Their combined capacity is 940 μF, and both are rated for 2,000 hours at 105 °C. The voltage rating is 400V, which is pretty close to the APFC’s DC bus voltage (approximately 380-400V DC). It would be better to use 420V-rated bulk caps or ideally 450V.
The APFC controller is a Champion CM6500UNX.
Four PingWei PWE120N65SFMF primary-switching FETs are used in a full-bridge topology, and an LLC resonant converter is employed for enhanced efficiency.
The LLC resonant controller is a Champion CM6901T6X.
The PSU’s main transformer. One of its main functions is to electrically isolate the primary and secondary sides.
Eight PingWei PWC013N04ES FETs regulate the 12V rail. This is the same number and type of FETs used in the 1000W model. They are installed on the business (top) side of the PCB.
Two DC-DC converters generate the minor rails. They use four UBIQ Semi QM3054M6 FETs. The PWM controller is an Anpec APW7159C.
Chemi-Con, Rubycon, and Nichicon provide the electrolytic capacitors. Toshin Kogyo and Chemi-Con make the polymer capacitors.
You can find more information about capacitor performance and other specs below:
The standby PWM controller is a KP22306AWG.
Several polymers and two big electrolytic caps on the face of the modular panel form an extra ripple-filtering layer.
The supervisor IC is an NDP NDP8313iKC (OVP, UVP, SCP, PG). This is the first time I’ve encountered this supervisor IC (to the best of my knowledge), and there is nothing for it online. I will ask CWT to provide some more info on it.
The soldering quality is generally decent; however, some large solder joints don’t look so nice. This is more of an aesthetic issue and won’t affect performance or reliability. In general, this is not CWT’s best job, that’s for sure.
The cooling fan is a CWT13525H12F-9 that uses a fluid-dynamic bearing.