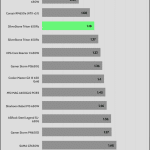
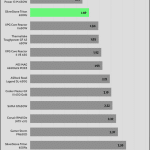
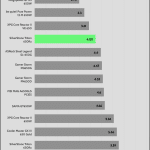
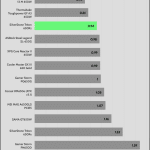
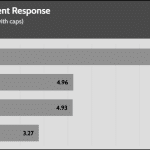
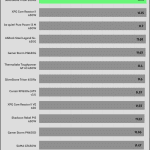
Transient Response
Transient response in power supplies refers to how quickly and effectively the PSU stabilizes its output voltage during sudden changes in load demand, such as when a CPU or GPU increases its power draw. It’s measured by the time and voltage deviation during these shifts. A faster, smaller transient response ensures stable power, preventing instability or damage to components.
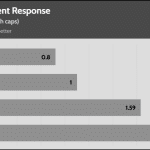
20% Load – 20ms
| Advanced Transient Response 20% - 50 Hz - No Caps | ||||
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
| 12V | 12.263V | 12.123V | 1.14% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.055V | 4.980V | 1.48% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.385V | 3.259V | 3.74% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.043V | 5.001V | 0.83% | Pass |
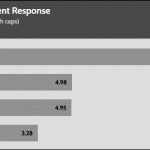
50% Load -20ms
| Advanced Transient Response 50% - 50 Hz - No Caps | ||||
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
| 12V | 12.249V | 12.100V | 1.21% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.031V | 4.946V | 1.70% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.363V | 3.217V | 4.35% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 4.993V | 4.941V | 1.04% | Pass |
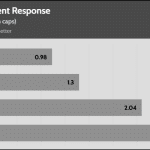
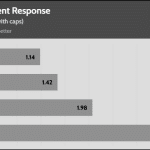
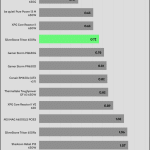
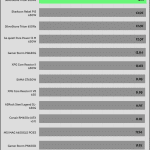
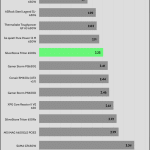
The transient response is good on all rails.
Transient Response ATX v3.1 Tests
The PSU passes all ATX v3.1 transient response tests.
The 12V rail’s performance is excellent at high loads.
Pages:




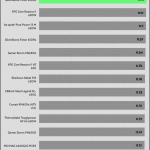
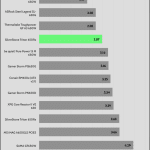
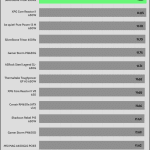
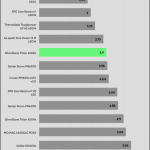

Fan is not of best quality, not ball bearing? Is the 109C temperature sensor reading on transformer?
Temperature the highest on the secondary side.