Protection Features
Desktop power supply units (PSUs) include several protection features to safeguard both the PSU itself and the connected PC components (motherboard, CPU, GPU, drives, etc.). These protections prevent damage from electrical faults, overloads, or abnormal conditions.
| OCP (Normal @ 27.6°C) | 12V: 100.20A (141.53%), 12.104V 5V: 30A (150.00%), 5.057V 3.3V: 29A (145.00%), 3.385V 5VSB: 6.5A (216.67%), 4.878V |
| OCP (Hot @ 44.0°C) | 12V: 99.40A (140.40%), 12.104V 5V: 30A (150.00%), 5.061V 3.3V: 29A (145.00%), 3.391V 5VSB: 6.4A (213.33%), 4.878V |
| OPP (Normal @ 28.1°C) | 1261.07W (148.36%) |
| OPP (Hot @ 42.8°C) | 1103.97W (129.88%) |
| OTP | ✓ (144°C @ Heat Sink) |
| SCP | 12V to Earth: ✓ 5V to Earth: ✓ 3.3V to Earth: ✓ 5VSB to Earth: ✓ -12V to Earth: ✓ |
| PWR_OK | Proper Operation |
| UVP (Full Load @ 90V) | ✓ |
| UVP (No Damage @ 80V) | ✓ |
| Conducted Emissions EN55032 & CISPR 32 | ✓ |
| NLO | ✓ |
| Fan Failure Protection | ✗ |
| SIP | Surge: MOV Inrush: NTC & Bypass Relay |
As in the 1000W model, the OCP triggering points are not correctly set to 12V. The difference between the normal and hot triggering points is too close, not effectively protecting the unit under high operating temperatures. Also, similar to the YT1200 and YT1000, the minor rails have high OCP triggering points compared to the nominal ratings, and to make matters worse, there is no difference in the triggering points between normal and high temperatures.
The over power triggering points are correctly set, with enough difference between normal and hot conditions. The remaining essential protection features are present and function well, except for fan failure protection, which is not implemented. Manufacturers must quickly realize that fan failure protection is crucial and begin implementing it in their designs.
EMC Pre-Compliance at a Glance
Every electronic device, including PSUs, can be an EMI source, and the amount of EMI it emits can affect the proper operation of nearby devices. EMI can, in some extreme cases, even render them unusable. Some standards have been established to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) noise. The corresponding standards for IT (Information Technology) products are CISPR 32 and its derivative, EN 55032, which applies to products sold in the EU. In the EU, every product bearing the “CE” marking must comply with EN 55032. CISPR 32 and EN 55032 standards categorize devices into two classes: A and B. Class B equipment is intended for domestic environments. Hence, its permitted EMI emissions are significantly lower than those of A-class devices.
Our equipment for EMI readings:
- Rohde & Schwarz FPC1500 (loaded with all options)
- Tekbox TBLC08 LISN
- Tekbox TBFL1 transient limiter
- Tekbox EMCview software
| CISPR 32 / EN55032 Limits | ||
| CISRP 32 / EN 55032 Class A Conducted EMI Limit | ||
| Frequency of Emission (MHz) | Conducted Limit (dBuV) | |
| Quasi-peak | Average | |
| 0.15 – 0.50 | 79 | 66 |
| 0.50 – 30.0 | 73 | 60 |
| CISPR 32 / EN 55032 Class B Conducted EMI Limit | ||
| Frequency of Emission (MHz) | Conducted Limit (dBuV) | |
| Quasi-peak | Average | |
| 0.15 – 0.50 | 66 – 56 | 56 – 46 |
| 0.50 – 5.00 | 56 | 46 |
| 5.00 – 30.00 | 60 | 50 |
| CISRP 32 / EN 55032 Class A 10-Meter Radiated EMI Limit | ||
| Frequency of Emission (MHz) | Field Strength Limit (dBuV/m) | |
| 30 – 88 | 39 | |
| 88 – 216 | 43.5 | |
| 216 – 960 | 46.5 | |
| > 960 | 49.5 | |
| CISRP 32 / EN 55032 Class B 3-Meter Radiated EMI Limit | ||
| Frequency of Emission (MHz) | Field Strength Limit (dBuV/m) | |
| 30 – 88 | 40 | |
| 88 – 216 | 43.5 | |
| 216 – 960 | 46.0 | |
| > 960 | 54.0 | |
Please note that the ATX spec allows a 4 dB margin for conducted and radiated emissions. This means that if a PSU exceeds the limits but stays within the 4 dB margin, it meets the corresponding ATX spec requirement (8.1 Emissions).
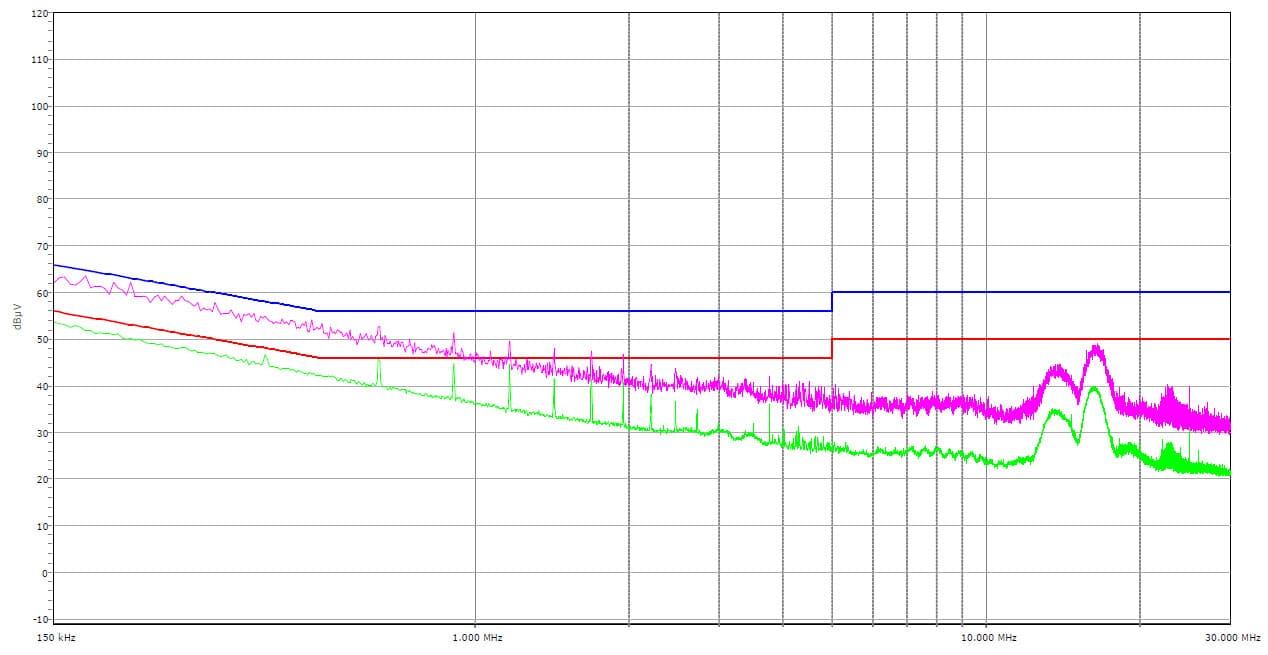
EMI Results
The PSU’s EMI emissions are under control, unlike the 1200W model.


Ares,Do you intend to test the new Redragon PSU RPGS 1000 watts & 1300 Watts Platinum PSUs?
I don’t have any contacts with the brand, sorry.