Transient Response
Transient response in power supplies refers to how quickly and effectively the PSU stabilizes its output voltage during sudden changes in load demand, such as when a CPU or GPU increases its power draw. It’s measured by the time and voltage deviation during these shifts. A faster, smaller transient response ensures stable power, preventing instability or damage to components.
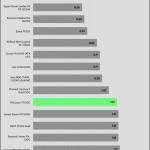
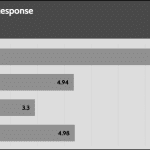
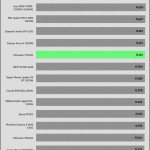
20% Load – 20ms
| Advanced Transient Response 20% - 50 Hz - No Caps | ||||
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
| 12V | 12.109V | 11.940V | 1.39% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.021V | 4.914V | 2.12% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.377V | 3.186V | 5.64% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.082V | 5.035V | 0.93% | Pass |
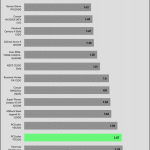
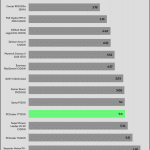
50% Load -20ms
| Advanced Transient Response 50% - 50 Hz - No Caps | ||||
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
| 12V | 12.078V | 11.973V | 0.87% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.014V | 4.913V | 2.02% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.368V | 3.170V | 5.89% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.047V | 5.001V | 0.92% | Pass |
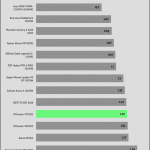
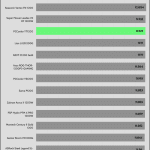
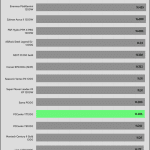
The transient response is average at 12V, and mediocre on the minor rails.
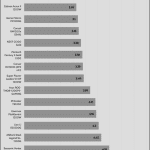
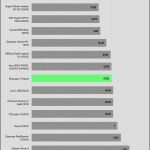
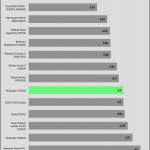
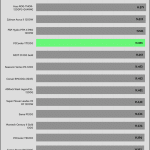
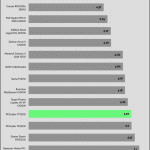
Transient Response ATX v3.1 Tests
[Note] For PSUs without a 12+4 pin connector, the maximum applied load for the transient response tests is 150%, rather than 200%.The PSU passes all ATX v3.1 transient response tests.
The 12V rail’s performance is average in these tests.
Pages: