Protection Features
Desktop power supply units (PSUs) include several protection features to safeguard both the PSU itself and the connected PC components (motherboard, CPU, GPU, drives, etc.). These protections prevent damage from electrical faults, overloads, or abnormal conditions.
| OCP (Cold @ 27°C) | 12V: 132.4A (132.4%), 12.165V 5V: 35.3A (141.2%), 5.002V 3.3V: 34.6A (138.4%), 3.299V 5VSB: 6.4A (213.33%), 5.004V |
| OCP (Hot @ 38°C) | 12V: 132A (132%), 12.174V 5V: 35.1A (140.4%), 5.001V 3.3V: 34.5A (138%), 3.299V 5VSB: 6.3A (210%), 5.004V |
| OPP (Cold @ 27°C) | 1595.71W (132.98%) |
| OPP (Hot @ 40°C) | 1491.06W (124.25%) |
| OTP | ✓ (135°C @ secondary side) |
| SCP | 12V to Earth: ✓ 5V to Earth: ✓ 3.3V to Earth: ✓ 5VSB to Earth: ✓ -12V to Earth: ✓ |
| PWR_OK | Proper operation |
| NLO | ✓ |
| Fan Failure Protection | ✗ |
| SIP | Surge: MOV Inrush: NTC Thermistor & Bypass relay |
The OCP triggering points are not highly set at 12V, but the difference between high and normal operating temperature is low, just 0.4A. To effectively protect the PSU, OCP triggering points need to be notably lower at high temperatures. The same is the case on the minor rails, which have high OCP triggering points and minimal differences between normal and high operating temperatures.
The over power triggering points are correctly set, with enough difference between normal and hot conditions. The rest of the essential protection features are present and function well, except for fan failure protection, which is not implemented. Manufacturers have to quickly realize that fan failure protection is crucial and start implementing it in their designs.
EMC Pre-Compliance at a Glance
Every electronic device, including PSUs, can be an EMI source, which, depending on the amount of EMI emitted, can affect the proper operation of nearby devices. EMI can, in some extreme cases, even render them unusable. Some standards have been established to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) noise. The corresponding standards for IT (Information Technology) products are CISPR 32 and its derivative, EN 55032, which applies to products sold in the EU. In the EU, every product bearing the “CE” marking must comply with the EN 55032 standard. CISPR 32 and EN 55032 standards categorize devices into two classes: A and B. Class B equipment is intended for domestic environments. Hence, its permitted EMI emissions are significantly lower than those of A-class devices.
Our equipment for EMI readings:
- Rohde & Schwarz FPC1500 (loaded with all options)
- Tekbox TBLC08 LISN
- Tekbox TBFL1 transient limiter
- Tekbox EMCview software
| CISPR 32 / EN55032 Limits | ||
| CISRP 32 / EN 55032 Class A Conducted EMI Limit | ||
| Frequency of Emission (MHz) | Conducted Limit (dBuV) | |
| Quasi-peak | Average | |
| 0.15 – 0.50 | 79 | 66 |
| 0.50 – 30.0 | 73 | 60 |
| CISPR 32 / EN 55032 Class B Conducted EMI Limit | ||
| Frequency of Emission (MHz) | Conducted Limit (dBuV) | |
| Quasi-peak | Average | |
| 0.15 – 0.50 | 66 – 56 | 56 – 46 |
| 0.50 – 5.00 | 56 | 46 |
| 5.00 – 30.00 | 60 | 50 |
| CISRP 32 / EN 55032 Class A 10-Meter Radiated EMI Limit | ||
| Frequency of Emission (MHz) | Field Strength Limit (dBuV/m) | |
| 30 – 88 | 39 | |
| 88 – 216 | 43.5 | |
| 216 – 960 | 46.5 | |
| > 960 | 49.5 | |
| CISRP 32 / EN 55032 Class B 3-Meter Radiated EMI Limit | ||
| Frequency of Emission (MHz) | Field Strength Limit (dBuV/m) | |
| 30 – 88 | 40 | |
| 88 – 216 | 43.5 | |
| 216 – 960 | 46.0 | |
| > 960 | 54.0 | |
Please note that the ATX spec allows a 4 dB margin for conducted and radiated emissions. This means that if a PSU exceeds the limits but stays within the 4 dB margin, it meets the corresponding ATX spec requirement (8.1 Emissions).
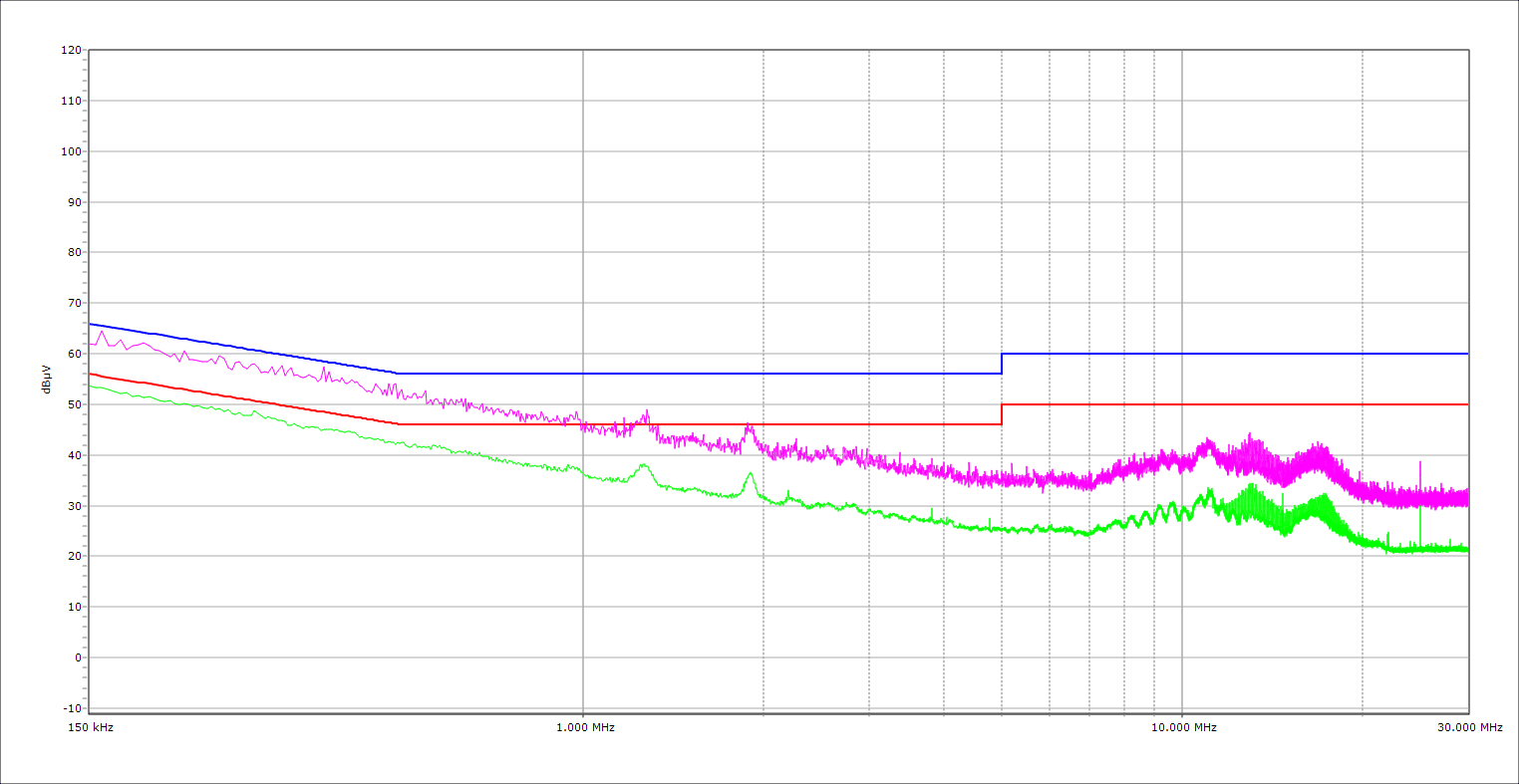
EMI Results
The PSU’s EMI emissions are under control.


Great review with balanced pros and cons! I really appreciate the detailed breakdown of ripple suppression, efficiency, and noise performance under different loads. Do you think firmware-level tuning could improve the transient response and OCP behavior, or is it more of a hardware limitation in this platform? telu jakarta
by mistake we left in the part analysis MCU etc. damn. I will fix it ASAP. This is NOT a digital platform.
Will you doing a review for the YS1000W version as well?
Hello Aris, i saw something strange in my country psu market, The Gamdias Helios P2 1300g & 1000g has cybenetics gold certification in the units sold in my country, but there’s nothing in cybenetics database about this brand
I have to send another note to Gamdias, as it seems, because they keep on using Cybenetics ratings without having them! Thank you for letting us know!
I hope they sent units for real certification in cybenetics… I also hope Redragon and risemode send units for certification. I don’t buy psu without cybenetics certification
Look it . I saw it, I thought it strange
https://www.kabum.com.br/produto/659749
Hello Aris, it seems that your review of the NZXT C1200 and C1000 is not accurate. The specifications on the Cybenetics site for the NZXT C1000 are listed here https://www.cybenetics.com/evaluations/psus/2448/, but on HW Busters it looks different; that is the NZXT C1200 https://hwbusters.com/psus/nzxt-c1200-atx-v3-1-psu-review/. I hope you can revise it soon. I am also waiting for news on several pending Cybenetics certification, such as the MSI A1250GS and some Gamemax Lioncore PSUs.
Hi Alex, what is wrong? It is typical of me to do some typos in the specs, but please point out what is different to save me some time.
because on your review on hwbusters the part analysis it’s should be NZXT C1000, just rechecked that NZXT C1000 should using this : https://hwbusters.com/psus/nzxt-c1000-atx-v3-1-psu-review/3/
General Data
Manufacturer (OEM) CWT
Platform CXT
PCB Type Double-Sided
Primary Side
Transient Filter 4x Y caps, 2x X caps, 2x CM chokes, 1x MOV
Inrush Protection 1x NTC Thermistor SCK207R0 (7Ω @ 25°C) & Relay
Bridge Rectifier(s)
2x GBJ2510 (700V, 25A @100°C)
APFC MOSFETs
2x Vishay SiHA105N60EF (600V, 8A @ 100°C, Rds(on): 0.102Ohm)
APFC Boost Diode
1x On Semi FFSP1065A (650V, 10A @ 152°C)
Bulk Cap(s)
2x Nippon Chemi-con ( 420V, 560uF each or 1120uF combined, 2000h @ 105°C, KMR)
Main Switchers
2x IPA60R125P6 (650V, 19A @ 100°C, Rds(on): 0.125Ohm)
APFC Controller
Champion CM6500UNX &
CM03X (for no load consumption)
Resonant Controller
Champion CM6901VAC
Topology
Primary side: APFC, Half-Bridge & LLC converter
Secondary side: Synchronous Rectification & DC-DC converters
Secondary Side
+12V MOSFETs 8x Infineon BSC014N04LS (40V, 125A @ 100°C, Rds(on): 1.4mOhm)
5V & 3.3V DC-DC Converters: 2x QM3054M6 (30V, 61A @ 100°C, Rds(on): 4.8mOhm) &
2x QN3107M6N (30V, 74A @ 100°C, Rds(on): 2.6mOhm)
PWM Controller(s): uP3861P
Filtering Capacitors Electrolytic:
4x Nippon Chemi-Con (W)
3x Rubycon (4-10,000 @ 105°C, YXF)Polymer: 31x FPCAPS, 1x Nippon Chemi-Con
Supervisor IC Weltrend WT7502 (OVD, UVD, PGO, )
Fan Model Hong Hua (HA13525H12SF-Z) (135mm, 12V, 0.5A Fluid Dynamic Bearing Fan)
5VSB
TVS Diode P6SMB
Rectifier
Pingwey R1MF
Synchronous Rectification Driver
Leadtrend LD8926AA1
Standby PWM Controller On-Bright OB2365T
based on this data NZXT C1000 on the cybenetics web should use this data, and that NZXT C1000 parts description data on Cybenetics web should belong to NZXT C1200
it seems your just misconfigured the parts description NZXT C1000 on cybenetics and using NZXT C1200 data, i see that you also don’t put the parts description of NZXT C1200 on cybenetics web, maybe you can revised up later
thank you, fixed it!
Is the review for the Hxi 1500 further delayed? Could you give me a rough estimate of when it might be ready?
into next week most likely.
So until Friday?