Transient Response
Transient response in power supplies refers to how quickly and effectively the PSU stabilizes its output voltage during sudden changes in load demand, such as when a CPU or GPU increases its power draw. It’s measured by the time and voltage deviation during these shifts. A faster, smaller transient response ensures stable power, preventing instability and component damage.
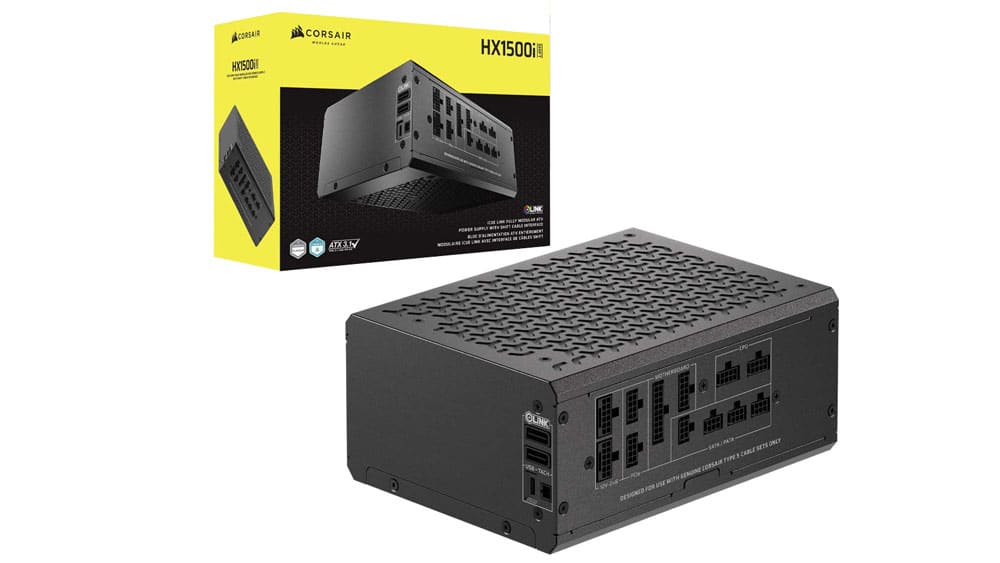
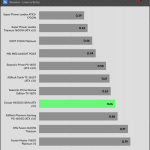
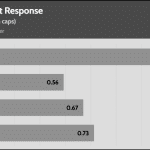
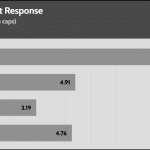
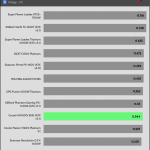
20% Load – 20ms
| Advanced Transient Response 20% - 50 Hz - No Caps | ||||
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
| 12V | 12.071V | 11.991V | 0.66% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.040V | 4.958V | 1.64% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.309V | 3.198V | 3.36% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 4.975V | 4.928V | 0.94% | Pass |
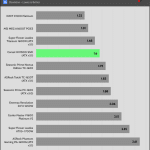
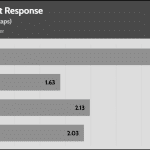
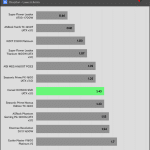
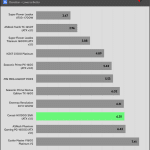
50% Load -20ms
| Advanced Transient Response 50% - 50 Hz - No Caps | ||||
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
| 12V | 12.046V | 11.967V | 0.65% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.035V | 4.956V | 1.56% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.303V | 3.187V | 3.50% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 4.955V | 4.910V | 0.91% | Pass |
The transient response at normal loads is good on all rails.
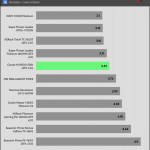
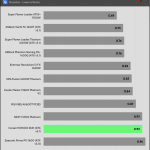
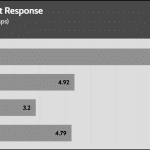
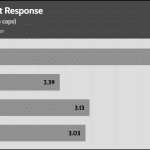
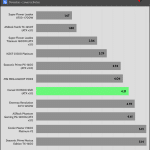
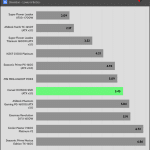
Transient Response ATX v3.1 Tests
[Note] For PSUs without a 12+4 pin connector, the maximum applied load for the transient response tests is 150%, rather than 200%.The PSU passes all ATX v3.1 transient response tests.
The 12V rail’s performance is low in these tests.
Pages:








The Aris is probably worth considering ask this. The EMI you tested on this power supply (I’m not an expert on this), is it worth buying, or will the EMI completely ruin this power supply and cause various problems? / Will you update this graph with new samples?
Best regards 🙂
Hi! There’s a controversy there because the OEM says EMI is ok in their measurements, while we found an issue. The problem is we have only 1x sample, so I told them to send several to check whether the problem is in my sample alone.
Hi Aris thanks for reply
So for now this corsair model do not buy or if i purchase same as you unit/batch it’s ok for PC components ?
You most likely won’t have any issues. But I need to figure what is going on.
Why only two 6+2 PCIE connectors? There should be at least three for high-end Radeon GPUs. Is this PSU exclusively for 5090 GPUs?
Most high-end PSUs care primarily for 12V-2×6 compatible GPUs, yes.
hello Aris did some FSP Vita GD PSU had an cybenetics evaluation report, i’ve seen this product have an cybenetics badge yet but i can’t find some data on a cybenetics web https://www.coolaler.com.tw/image/fsp/vita_gd_650w/01.jpg ?
Hi! Cyben has tested them, they just didn’t go public. I will talk to FSP now!
And also needs update for MSI A1250GS https://www.msi.com/Power-Supply/MPG-A1250GS-PCIE5/Overview because i can’t find them on cybenetics web mate thx
This is still under test. We asked for new samples.
I’ve bought HX1500i Shift 2 days after it went on sale. Now one week in and so far so good. Included software, at my near idle load of 160W, shows 88% efficiency which is kind of disappointing. AX1600i at the same load had 94% efficiency, but space was an issue with cables directed to the front = “the normal way”. Those made my plans to build custom LC setup on-hold. HX has the same dimensions but most of the cables are now directed to the side of the case. And here is one more drawback it has – the USB (for communication with motherboard), TACH (for Corsair’s AIO pump) and iCUE LINK (for RGB) connectors are directed to the front! This makes no sense at all. It’s like the entire PCB for this part was done as an afterthought. All of those should be on the side as well. Coirsair is including flat 90 deg iCUE connector, but for USB-C you have to buy an 90 degree adapter on your own. Another thing is the cables that are included are not sleeved, instead they used some kind of rubbery polymer with marks that pretend to give of sleeved visuals. 8-pin PCIe cable also has this ugly loop to the +2 pins just next to the plug because it’s 6 wires but the plug has 8 connectors (they extended from 6 to additional 2 just next to GPU’s plug and it’s really ugly). But hey they probably saved 10 cents on the wires! Any noises, coils, crickets or whatever – I don’t hear anything like that. But I still suggest to setup fan to do the minimal spin (15% setting is like 450RPM) so the electronics inside operates in lower temp and has longer lifespan.
One more thing I noticed, it may be just my imagination, but I have 4 enterprise class high capacity WD HDD’s and when I turn on the PC it gives of of feeling like it now takes longer time for the HDD’s to reach the operating speed. Maybe it’s in-rush load handling or something (I could try and measure the current on the rig, but I doubt my $5 multimeter will catch anything useful).
Also one more thing to note. I’ve bought it on October 15. All the promo materials on Corsair website (both English version and my native language site version) were showing that it has Cybenetics Platinum certificate. Even when I visited Corsair website one day earlier it was the same. However when I checked Cybenetics certification website nothing was there for HX1500i Shift. There was only the regular HX1500i listed. And now certificate is present but the date on it is 17 October.
A very disappointing PSU… can you say what’s next on the list?
Thermaltake Toughpower PT
I mean 0.928… I typed it wrong
Hello Aris, I think there’s a small mistake in the Pcyes Aether 1000W certification. At 230V the certification shows Cybernetics Silver, but it has an efficiency of 90.459% at 230V, a little below
Please note that efficiency levels also depend on other factors, such as PF and 5VSB efficiency, as well as vampire power, in addition to overall efficiency.
Hmm. I didn’t know that. I thought 89-91% was considered gold at 230V, I didn’t know there were other details.
That’s the PSU I was talking about. https://www.cybenetics.com/evaluations/psus/2434/
I checked, you’re totally right. Her overall efficiency is gold and the Vsb efficiency is also above 75%, but her PF is below 0.930 (gold), hers is at 0.929. I hope they fix this… Thank you very much and I apologize for the inconvenience.
I mean 0.928… I typed it wrong