Transient Response
Transient response in power supplies refers to how quickly and effectively the PSU stabilizes its output voltage during sudden changes in load demand, such as when a CPU or GPU increases its power draw. It’s measured by the time and voltage deviation during these shifts. A faster, smaller transient response ensures stable power, preventing instability and component damage.
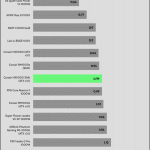
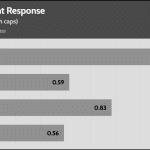
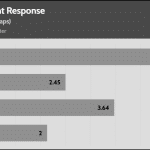
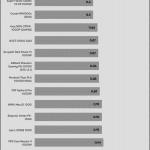
20% Load – 20ms
| Advanced Transient Response 20% - 50 Hz - No Caps | ||||
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
| 12V | 12.054V | 11.936V | 0.98% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.093V | 5.008V | 1.68% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.402V | 3.273V | 3.78% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.060V | 5.014V | 0.91% | Pass |
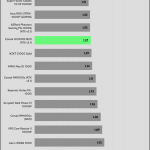
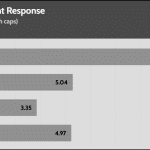
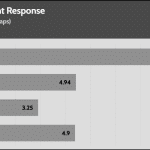
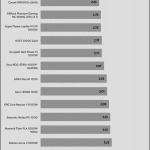
50% Load -20ms
| Advanced Transient Response 50% - 50 Hz - No Caps | ||||
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
| 12V | 12.015V | 11.895V | 1.00% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.086V | 5.012V | 1.45% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.394V | 3.264V | 3.85% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.039V | 4.996V | 0.86% | Pass |
The transient response at normal loads is good on all rails.
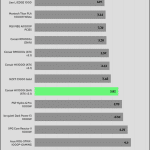
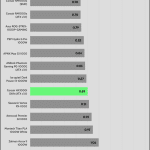
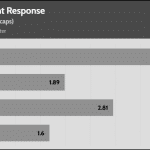
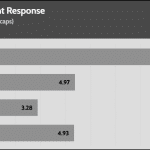
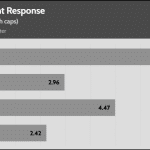
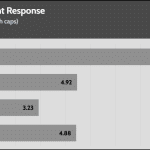
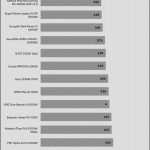
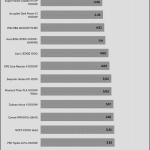
Transient Response ATX v3.1 Tests
[Note] For PSUs without a 12+4 pin connector, the maximum applied load for the transient response tests is 150%, rather than 200%.The PSU passes all ATX v3.1 transient response tests, but it is barely passing at the 200% transient response load.
The 12V rail’s performance is dead low in these tests.
Pages:






Ares,Do you intend to test the Rise mode PSU Zeus 1000 watts & 850 Watts PSUs?.
They performed very well on teclab tests, i think they would get a good certification in cybenetics.com if tested
Hi! I don’t have any contacts with this brand, sorry.