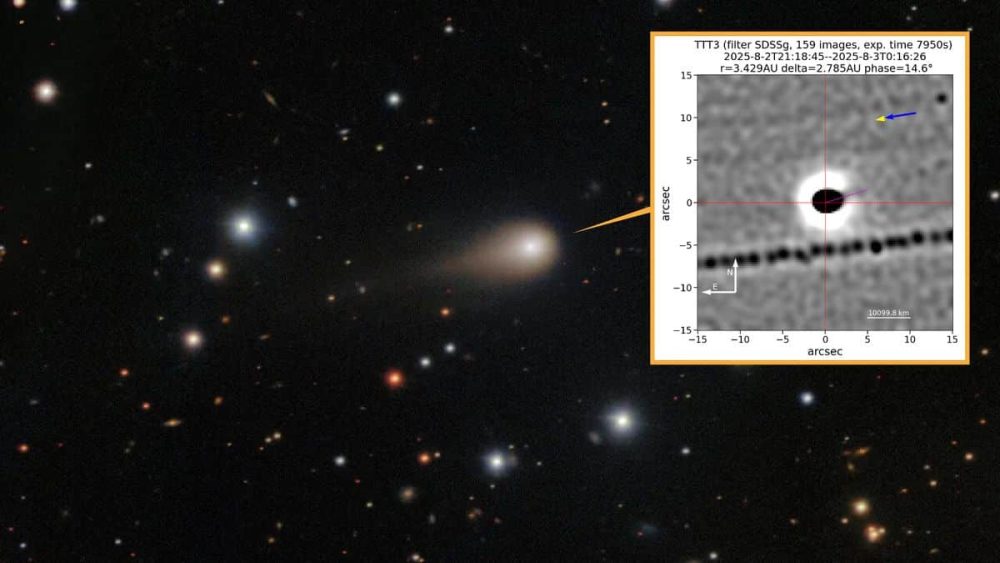
A mysterious interstellar object known as 3I/ATLAS, roughly the size of Manhattan, has drawn the attention of NASA’s International Asteroid Warning Network (IAWN), sparking both scientific curiosity and public speculation about its true nature.
First detected on July 1, the object is traveling at nearly twice the speed of previous interstellar visitors such as ‘Oumuamua and Borisov. Its unusual characteristics have prompted a formal observation campaign by IAWN, a global coalition of space experts tasked with monitoring potential threats to Earth.
Unprecedented Behavior Raises Questions
3I/ATLAS has displayed a series of anomalies that defy typical comet behavior:
- An anti-tail—a jet of particles pointing toward the sun, contrary to normal cometary tails.
- Emission of a rare alloy, nickel tetracarbonyl, at a rate of 4 grams per second, with no detectable iron—a composition previously associated only with industrial processes on Earth.
- Non-gravitational acceleration and an anomalous trajectory that will bring it unusually close to Jupiter, Venus, and Mars.
These peculiarities have led some scientists, including Harvard astrophysicist Professor Avi Loeb, to suggest the object may not be natural. In a recent blog post, Loeb speculated that 3I/ATLAS could be an alien probe using the sun’s gravity to adjust its speed and trajectory.
Scientific Response: Observation Over Alarm
In response, IAWN has launched a “comet campaign” scheduled from November 27 to January 27. The initiative aims to refine detection techniques and improve accuracy in tracking the object’s path. A workshop will be held to train participants in advanced astrometry methods.
While the campaign is framed as a training exercise, Loeb suggests the attention signals deeper concerns. “If 3I/ATLAS is a massive mothership,” he wrote, “it will likely continue along its original gravitational path and ultimately exit the solar system.”
Public Intrigue and Speculation
The object has also stirred discussion online, with social media users questioning whether authorities are downplaying its potential significance. Loeb further fueled speculation by recently advising people to “take vacations before October 29,” hinting that NASA may not be sharing all available data.
Despite the buzz, most astronomers urge caution, noting that unusual chemical or orbital properties do not necessarily imply an artificial origin. Natural explanations—such as unique composition or solar interaction—remain plausible.
What’s Next?
3I/ATLAS is expected to make its closest approach to the sun in the coming days, soon slipping from view. Whether it’s a natural oddity or something more, its study offers a rare opportunity to improve planetary defense capabilities and deepen our understanding of objects from beyond our solar system.