Part Analysis
The main parts of the graphics card are the backplate, the cooler, the PCB, and the fan assembly.
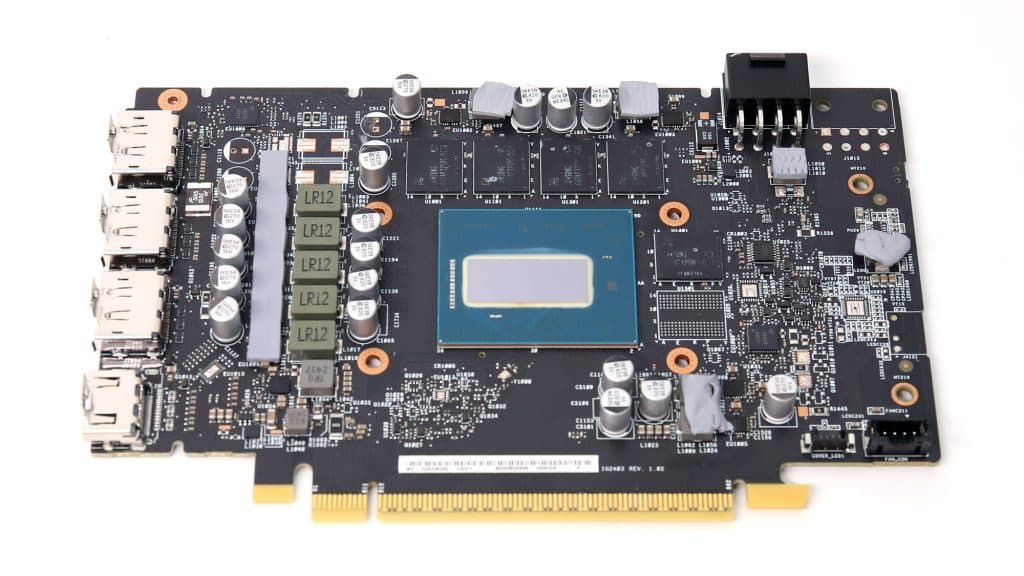
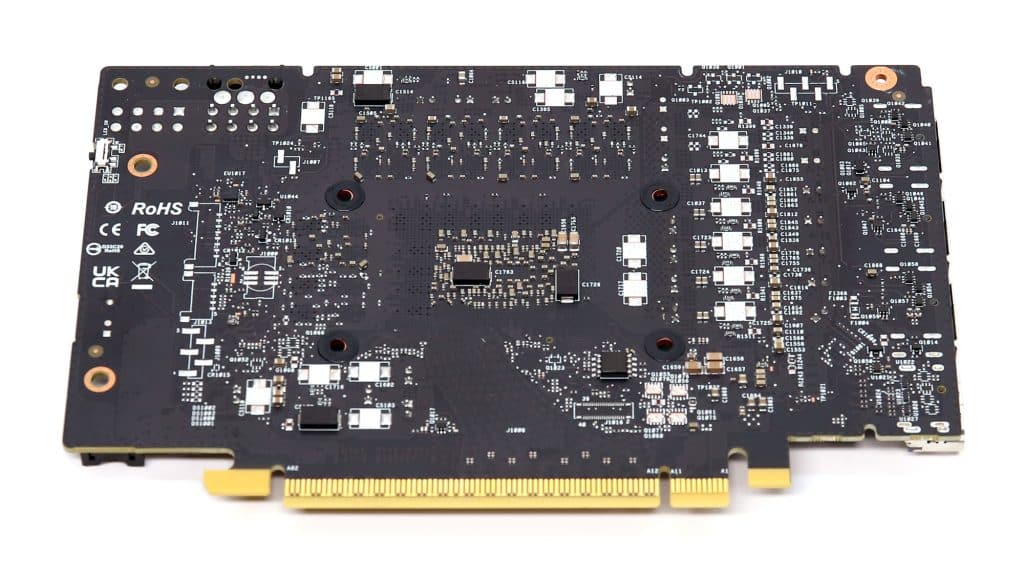
Photos of the PCB’s front and rear sides.
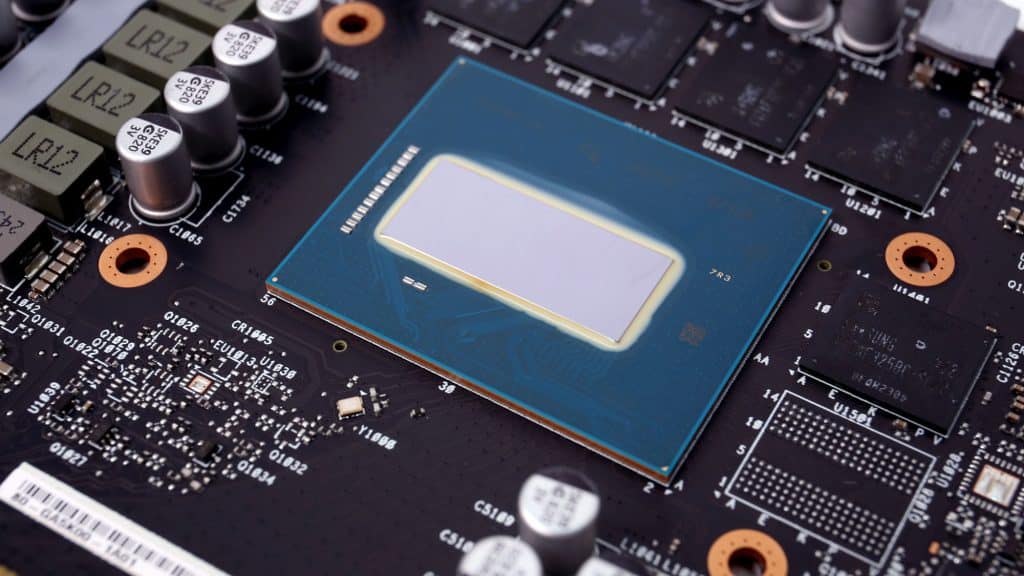
The cooling solution uses seven heatpipes, which pass through the block that comes in contact with the GPU.
The fans’ model number is FDC10U12S9-C. They are pretty strong, with a 0.45A max current rating. I couldn’t find any reliable information about their bearings, and I didn’t want to destroy them to find that out, either.
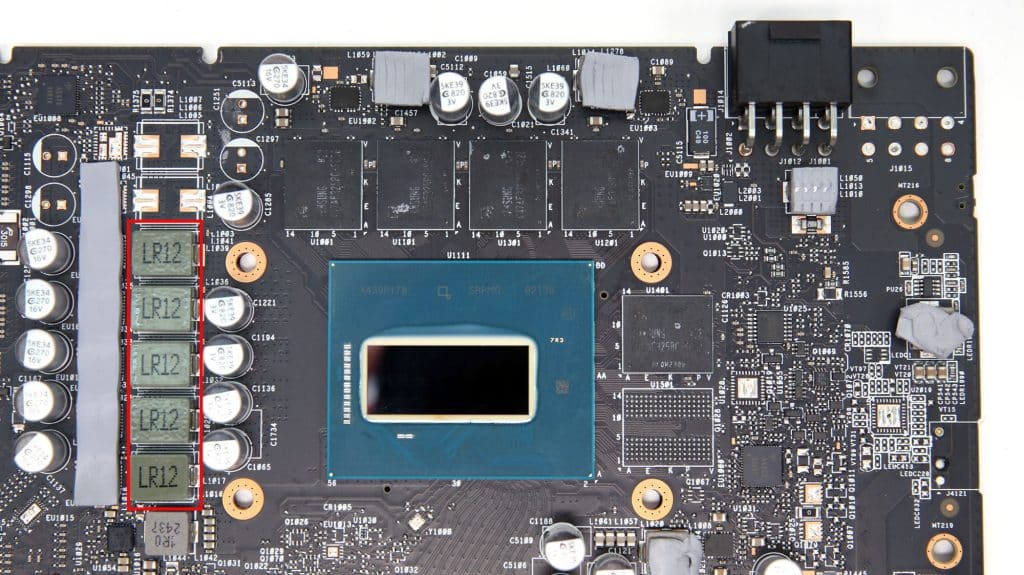
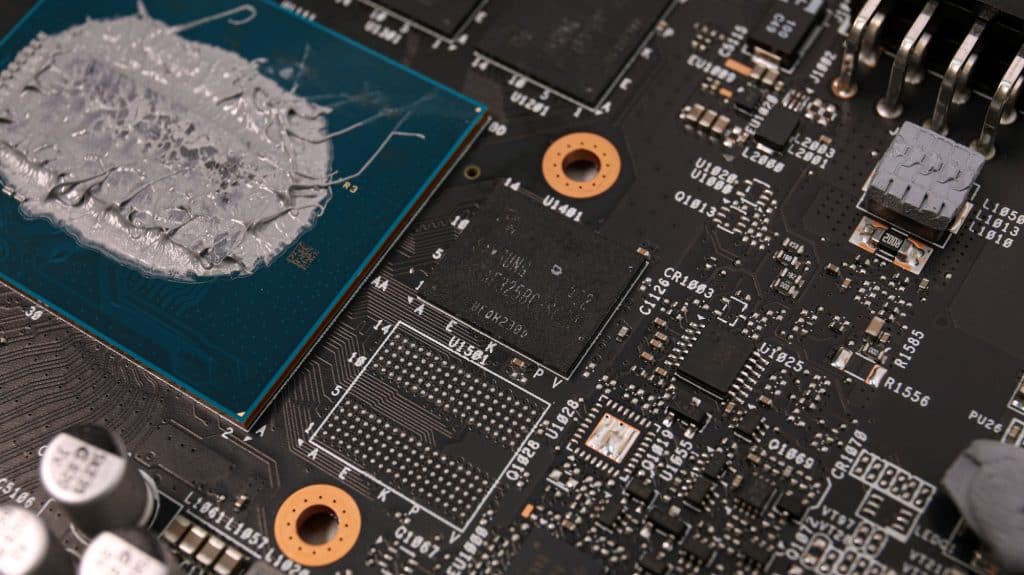
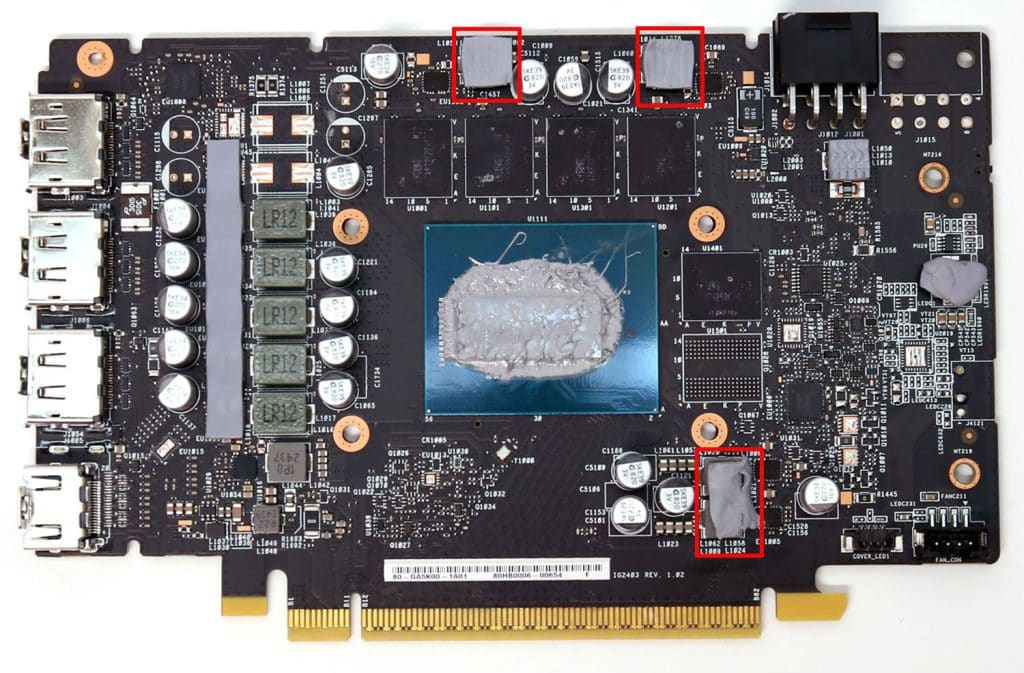
A five-phase VRM circuit handles the GPU’s power delivery. The same circuit uses Alpha & Omega AOZ5517QI DrMOS, and the PWM controller is an Alpha & Omega AOZ71137QI IC.
Samsung makes the GDDR6 memory chips, which have a model number of K4ZAF325BC-SC20. They can typically operate at 2500 MHz, 20 Gbps GDDR6 effective.
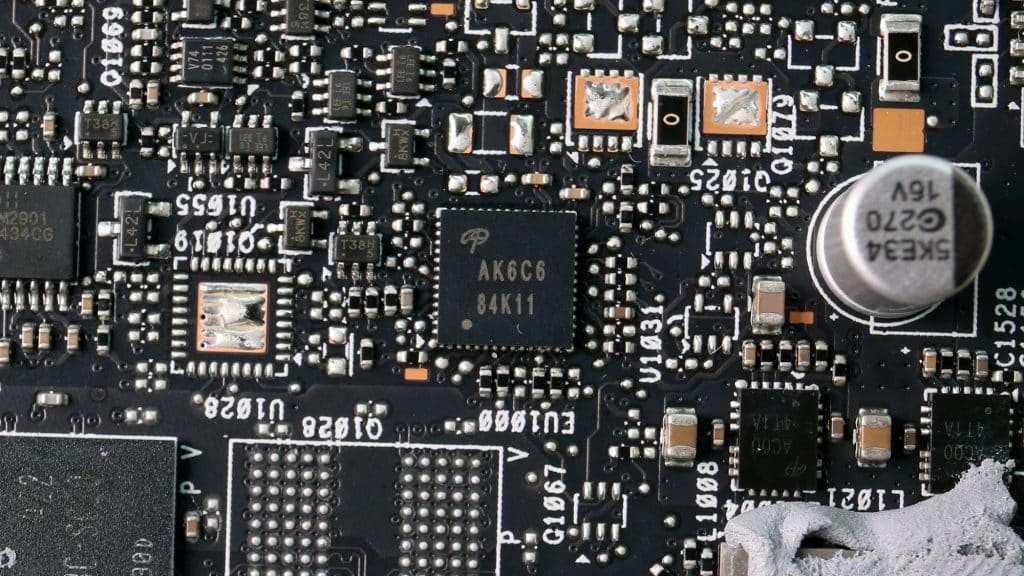
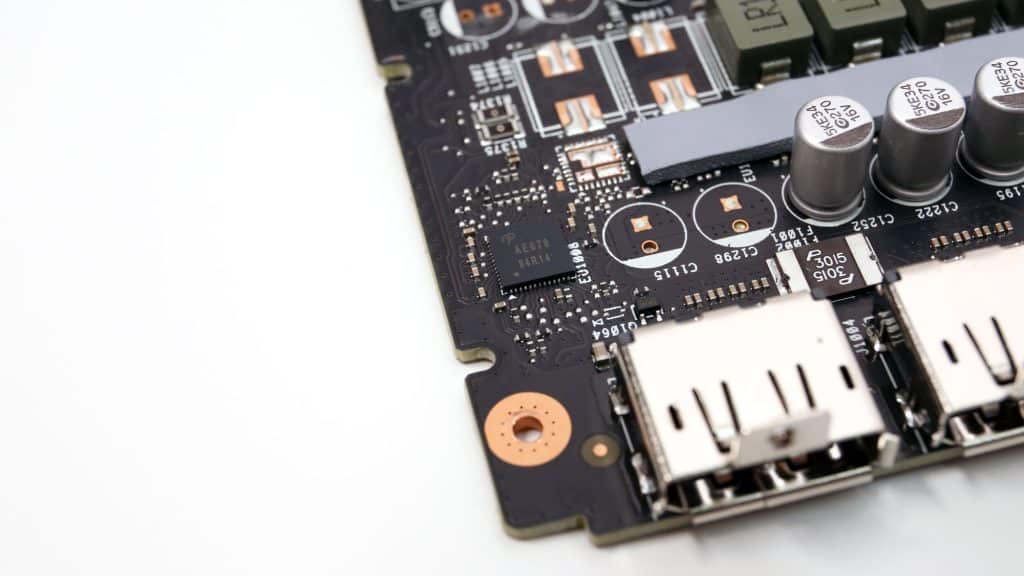
RAM takes power from two VRMs, handled by an Alpha & Omega controller. The RAM voltage regulation circuit uses Alpha and Omega AOZ5507QI DrMOS.
The card’s power socket. It is a plain 6+2 pin PCIe header.
Apaq provides the polymer capacitors used by the PCB’s VRMs.
- Prologue & Technical specifications
- Intel’s Key Technologies
- Box & Contents
- Part Analysis
- Specifications Comparison
- Test System
- Game Benchmark Details
- Raster Performance
- RT Performance
- RT Performance + DLSS/FSR/XeSS Balanced
- Raytracing Performance + DLSS/FSR/XeSS Balanced + FG
- DLSS/FSR/XeSS Balanced (No RT)
- DLSS/FSR/XeSS Balanced + FG (No RT)
- Relative Perf & Perf Per Watt (Raster)
- Relative Perf & Perf Per Watt (Raster + DLSS/FSR/XeSS)
- Relative Perf & Perf Per Watt (RT)
- Relative Perf & Perf Per Watt (RT + DLSS/FSR/XeSS)
- Relative Perf & Perf Per Watt (RT + DLSS/FSR/XeSS + FG)
- Rendering Performance
- Operating Temperatures
- Operating Noise & Frequency Analysis
- Power Consumption
- Clock Speeds & Overclocking
- Cooling Performance
- Epilogue