Battlemage Architecture
Here is a video by Intel to learn more about the Battlemage architecture details.
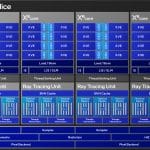
The Intel Arc B-Series GPUs use Intel’s latest Xe2 architecture, optimized to deliver improved efficiency and higher performance per core with less software overhead. Second-generation Xe-cores deliver the solid compute capabilities required for modern workloads, including high-performance XMX AI engines. More capable ray tracing units support new Xe-cores, better mesh shading performance, and improved support of key graphics functions to significantly increase performance efficiency with the latest game engines.
Intel used TSMC for Battlemage and, more specifically, the TSMC N5 process node, while the previous Alchemist used the N6 process node. The BMG GPU has fewer transistors than the ACM-G10 (19.6B vs. 21.7B), so combined with the lower process node, the die size is much smaller.
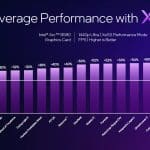
According to Intel, the Arc B-Series GPUs offer 70% better performance per Xe-core3 and 50% more performance per watt than the previous generation. The B580 GPU, compared to the Arc A750 GPU, is, on average, 24% faster at 1440p, with some games up to 78% faster.
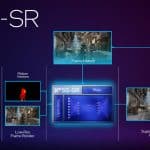
About XeSS 2
XeSS 2 now includes three technologies:
- XeSS Super Resolution
- XeSS Frame Generation
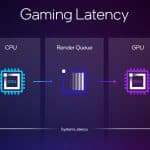
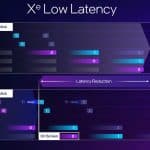
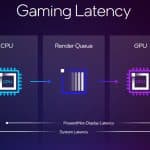
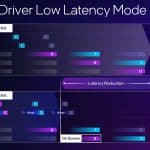
- Xe Low Latency
XeSS Super Resolution is the key technology underpinning first-generation XeSS, which has offered AI-based upscaling for over two years and now supports more than 150 games. New AI-powered XeSS Frame Generation adds interpolated frames using optical flow and motion vector reprojection to provide higher fluidity gaming. The new Xe Low Latency integrates with the game engine to respond faster to gamers’ inputs. With all three technologies activated, XeSS 2 can increase the frames-per-second output by up to 3.9x to deliver high performance in demanding AAA games.
XeSS Super Resolution
XeSS Frame Generation
Xe Low Latency
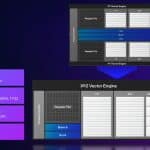
Xe Matrix Extensions AI Engine
Intel’s all-in-one, free AI starter application is designed to run generative AI workloads locally. It allows users to efficiently generate text-to-image, edit photos, upscale, and customize chatbots with their data.
Graphics Software
The software supporting Intel’s dedicated graphics cards is already mature, providing many options, including overclocking, and it is frequently updated.
- Prologue & Technical specifications
- Intel’s Key Technologies
- Box & Contents
- Part Analysis
- Specifications Comparison
- Test System
- Game Benchmark Details
- Raster Performance
- RT Performance
- RT Performance + DLSS/FSR/XeSS Balanced
- Raytracing Performance + DLSS/FSR/XeSS Balanced + FG
- DLSS/FSR/XeSS Balanced (No RT)
- DLSS/FSR/XeSS Balanced + FG (No RT)
- Relative Perf & Perf Per Watt (Raster)
- Relative Perf & Perf Per Watt (Raster + DLSS/FSR/XeSS)
- Relative Perf & Perf Per Watt (RT)
- Relative Perf & Perf Per Watt (RT + DLSS/FSR/XeSS)
- Relative Perf & Perf Per Watt (RT + DLSS/FSR/XeSS + FG)
- Rendering Performance
- Operating Temperatures
- Operating Noise & Frequency Analysis
- Power Consumption
- Clock Speeds & Overclocking
- Cooling Performance
- Epilogue