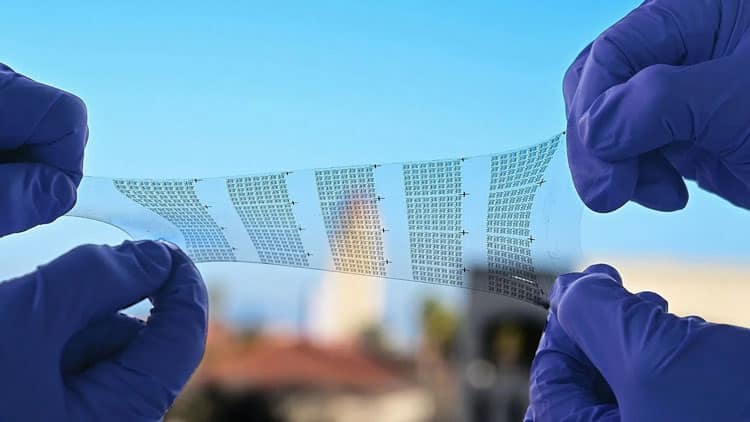
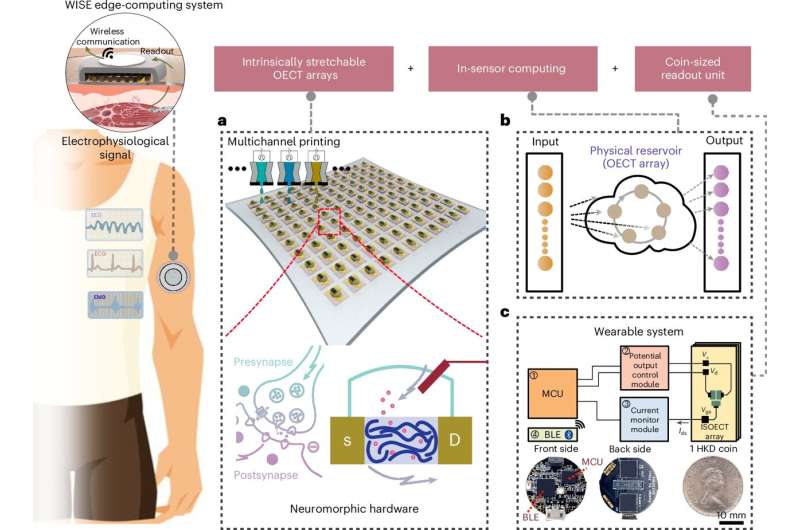
Researchers at the University of Hong Kong have developed groundbreaking wearable technology that could change our perception of health monitoring and smart devices. These stretchable transistors, called Organic Electrochemical Transistors (OECTs), are made from flexible, skin-friendly materials, allowing them to work seamlessly in devices like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and even medical sensors.
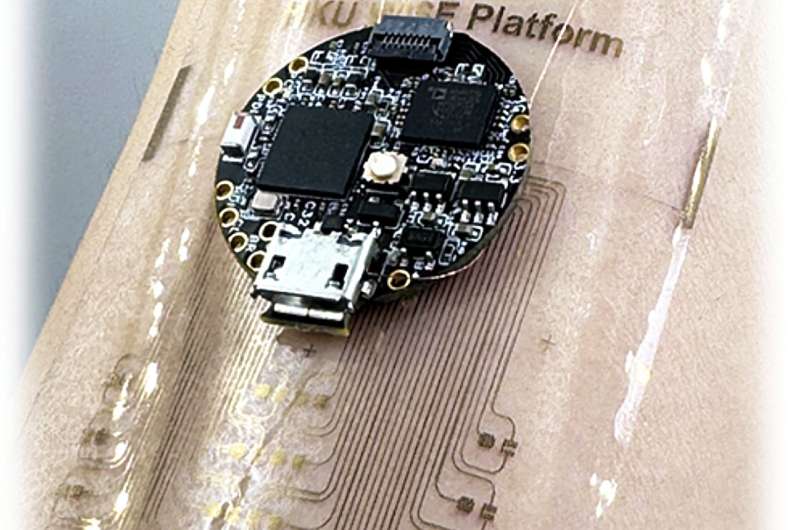

Unlike conventional transistors, which are often stiff and uncomfortable to wear, these stretchable transistors can bend and stretch, making them perfect for wearables that must fit comfortably on the human body. They can also function in wet or humid conditions, which is a game-changer for devices used in medical applications or during workouts.
What makes this technology genuinely innovative is its ability to perform real-time AI-driven computations directly on the device—this is called edge computing. This means the device doesn’t need to send data to external servers for processing. Instead, it can analyze information and make decisions instantly on the user’s wrist. This could lead to faster, more accurate health monitoring, alerting users or doctors to potential issues like abnormal heart rates or muscle fatigue before they become serious.
The researchers believe this technology could significantly improve digital health by providing more accurate data and faster responses, especially for those managing chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease. But it doesn’t stop there—the same technology could also be applied in other fields, like sports, where real-time tracking of muscle activity could help athletes optimize their performance, and even workplace safety, where wearables could monitor workers in hazardous conditions to prevent accidents.
The research team behind this breakthrough envisions a future where AI-powered wearables are used across sectors to improve everything from health outcomes to sports performance and military readiness. With the ability to stretch and conform to the body, these devices could become essential companions in our daily lives, offering us real-time insights into our health, safety, and performance.
Stretchable OECT technology is a breakthrough in the wearables field, enabling the collection of physiological data and real-time, AI-powered edge computing directly on the device. Here’s how this tech could be applied across different sectors:
Healthcare: Revolutionizing Remote Monitoring & Diagnosis
The primary application of these OECT-based devices would likely be in healthcare, where wearables can monitor vital signs, detect health anomalies, and even assist in managing chronic diseases like diabetes or heart conditions. The critical advantage is real-time decision-making at the edge, meaning data doesn’t need to be sent to external servers for analysis, which reduces latency and enhances privacy.
- Continuous Monitoring: Devices could accurately monitor patient conditions (heart rate, blood oxygen levels, muscle activity) and immediately alert users or healthcare providers of abnormalities. This could be invaluable for early detection of heart attacks, strokes, or other life-threatening events.
- Closed-Loop Therapeutics: The tech could also enable closed-loop systems that automatically adjust treatments. For example, insulin pumps for people with diabetes could respond to fluctuating glucose levels in real time, or pain-management devices could release medication based on physiological feedback.
Sports and Fitness: Precision Tracking and Injury Prevention
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, stretchable wearables would allow for highly accurate monitoring of body movements, muscle activation, and fatigue. AI-driven insights can enhance training by analyzing the biomechanical data collected in real time.
Performance Optimization: Real-time data on muscle engagement and energy expenditure could help athletes optimize their training sessions. Wearables could offer immediate feedback on form, helping prevent injuries.
Rehabilitation and Recovery: In rehabilitation, especially after surgery or injury, wearable devices can track progress and ensure that exercises are performed correctly. Stretchable wearables could even be used during aquatic therapy, as they remain functional in wet environments.
Workplace Safety: Monitoring Workers in Hazardous Environments
In industries where workers are exposed to hazardous conditions (e.g., construction, mining, firefighting), these wearable sensors could monitor physiological conditions such as fatigue, stress, and exposure to harmful substances. Alerts could be triggered in real-time if a worker’s vital signs indicate potential danger.
Preventing Accidents
For example, a wearable could monitor a worker’s hydration levels or stress response and issue warnings before exhaustion leads to mistakes. Stretchability and durability allow these wearables to be comfortable during physically demanding work.
Gaming and Entertainment: Enhancing Immersive Experiences
In gaming, stretchable wearables could provide precise gesture and movement tracking, enhancing the virtual and augmented reality experience. Imagine a game that responds to your muscle contractions, posture, and hand gestures with real-time precision.
- Motion Capture for VR/AR: Stretchable transistors could improve the realism and accuracy of motion capture systems, allowing for more immersive gaming experiences.
- Haptic Feedback: The ability to create flexible electronics could also lead to wearables that offer advanced haptic feedback, increasing immersion in virtual environments.
- AI & Data Analysis: Personal Edge Computing
Incorporating AI-driven edge computing directly into these devices allows them to make quick, autonomous decisions. In intelligent cities or environmental monitoring sectors, these wearables could also track ecological factors (e.g., air quality, temperature) and use AI to analyze and predict trends without transmitting the data to the cloud.
Health and Fitness AI
Personalized AI-driven insights could be provided to users without external data processing, enhancing privacy and security while delivering customized recommendations.
Military and Tactical Applications: Enhancing Soldier Performance
In the military, stretchable wearables could monitor soldiers’ physiological status during missions, tracking fatigue, hydration, and stress levels. Real-time analytics could provide commanders vital information for troop health and readiness decisions. The tech’s durability in extreme conditions would also make it suitable for harsh environments like deserts, jungles, or cold climates.
My Take on the Future
The potential for organic electrochemical transistors (OECTs) in wearable devices is vast, as it merges real-time analytics with highly personalized healthcare and other applications. This technology could be a game changer, especially in preventive healthcare and occupational safety, where immediate action is required. Additionally, these devices are stretchable, flexible, and comfortable, so they could see widespread adoption, opening doors to more advanced wearables in everyday life.
The combination of flexibility, neuromorphic computing, and real-time AI at the edge could enable wearables to become intelligent, continuous companions that enhance human performance and well-being across many fields.


